SmaCC Tutorial
This is a walk-through tutorial to demonstrate some features of SmaCC, the Smalltalk Compiler Compiler, as we incrementally develop a simple calculator. If you haven't already done so, you will first need to load the source. Once you have loaded the code, you need to open the SmaCC Parser Generator. In VisualWorks, it is under Tools menu. Dolphin has it in the additional tools folder. Here's the UI running under Dolphin:
Our first calculator is going to be relatively simple. It is going to take two numbers and add them together. To start things off, we have to tell the scanner how to recognize a number. It starts with one or more digits, possibly followed by an decimal point with zero or more digits after it. The scanner definition for this token is:
<number> : [0-9]+ (\. [0-9]*) ? ;
Let's go over each part:
| Expression | Description |
| <number> | Names the token. The name inside the <> must be a legal Smalltalk variable name. |
| : | Separates the name of the token from the token's definition. |
| [0-9] | Matches any single character in the range '0' to '9' (a digit). We could also use \d or <isDigit> as these also match digits. |
| + | Matches the previous expression one or more times. In this case, we are matching one or more digits. |
| ( ... ) | Groups subexpressions. In this case we are grouping the decimal point and the numbers following the decimal point. |
| \. | Matches the '.' character (. has a special meaning in regular expressions, \ quotes it). |
| * | Matches the previous expression zero or more times. |
| ? | Matches the previous expression zero or one time (i.e., it is optional). |
| ; | Terminates a token specification. |
We don't want to have to worry about whitespace in our language, so we need to define what a whitespace is and to ignore it. To do this, enter the following token specification on the next line:
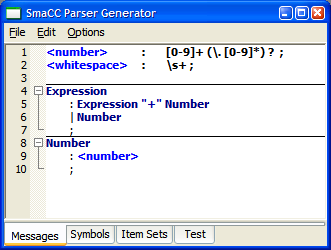
<whitespace> : \s+;
\s matches any whitespace character (space, tab, linefeed, etc.). So how do we tell the scanner to ignore it? If you look in the SmaCCScanner class, you will find a method named #whitespace. If a scanner understands a method that has the same name as a token name, that method will get called whenever the scanner matches that kind of token. As you can see, the SmaCCScanner>>whitespace method eats whitespace. There is also a #comment method that behaves similarly. However, the SmaCCScanner>>comment method also stores the interval in the source where the comment occurred in the comments instance variable.
The only other token that will appear in our system would be the '+' token for addition. However, since this is token is always the same, we can enter it directly in our production rules.
Speaking of our grammar, let's go ahead and define it. Enter the following specification below your two previous rules:
Expression : Expression "+" Number | Number ; Number : <number> ;
This basically says that an expressions is either a number or an expression added to a number. You should now have something that looks like:
We should be able to compile a parser now. First, we need to specify the scanner and parser classes to create. These are entered from the Options -- Scanner Class and Parser Class menu options. Use CalculatorScanner and CalculatorParser respectively. Once the class names are entered, we are ready to compile the parser. Select File Save or hit Ctrl+Shift+S. This will create new Smalltalk classes for the CalculatorScanner and CalculatorParser and compile several methods in those classes. All methods that SmaCC compiles will go into a "generated-*" method protocol. You should not change those methods or add new methods to the "generated-*" method protocols since they are replaced or deleted each time you compile.
Whenever SmaCC creates new classes, they are compiled in the default application/package. You may wish to set the default package before you compile.
Now we are ready to test our parser. Go to the "test" pane, enter "3 + 4", and select "Evaluate" popup menu option; you will see that the parser correctly parses it. If you press "Inspect" you will see and inspector on an OrderedCollection that contains the parsed tokens. This is because we haven't specified what the parser is supposed to do when it parses. You can also enter incorrect items. For example, try to parse "3 + + 4" or "3 + a". An error message should appear in the text.
If you are interested in the generated parser, you may wish to look at the output from compiling the parser in the Symbols or Item Sets tab. The Symbols tab lists all of the terminal and non-terminal symbols that were used in the parser. The number besides each is the internal id used by the parser. The Item Sets tab lists the LR item sets that were used in the parser. These are printed in a format that is similar to the format used by many text books. The Messages tab is used to display any warnings generated while the parser was compiled. The most common warning is for ambiguous actions.
Now we need to define the actions that need to happen when we parse our expressions. Currently, our parser is just validating that the expression is a bunch of numbers added together. Generally, you will create some structure that represents what you've parsed (e.g., a parse tree). However, in this case, we are not concerned about the structure, but we are concerned about the result (the value of the expression). For our example, you need to modify the grammar definition to be:
Expression
: Expression "+" Number {'1' + '3'}
| Number {'1'}
;
Number
: <number> {'1' value asNumber}
;
The text between the braces is Smalltalk code that gets evaluated when the rule is applied. Strings with a number get replaced with the corresponding expression in the production. In the first Expression rule, the '1' will get replaced by the object that matches Expression and the '3' gets replaced by the object that matches Number. The second item in the rule is the "+" token. Since we already know what it is, it is not interesting. Compile the new parser. Now when you do a 'Inspect' from the test pane containing "3 + 4", you should see the result: 7.
One problem with the previous example is that if you need to change a rule then you may also need to change the code for that rule. For example, suppose you inserted a new token at the beginning of a rule, then you would need to change all of your references in the Smalltalk code. We can alleviate this problem by using named expressions. After each part of a rule, we can specify its name. Names are specified with single quotes and must be legal Smalltalk variable names. Doing this for our grammar we get:
Expression
: Expression 'expression' "+" Number 'number' {expression + number}
| Number 'number' {number}
;
Number
: <number> 'numberToken' {numberToken value asNumber}
;
While this will result in the same language being parsed, it makes it easier to maintain your parsers. Let's extend our language to add subtraction. Here's the new grammar:
Expression
: Expression 'expression' "+" Number 'number' {expression + number}
| Expression 'expression' "-" Number 'number' {expression - number}
| Number 'number' {number}
;
Number
: <number> 'numberToken' {numberToken value asNumber}
;
After you've compiled this, '3 + 4 - 2 ' should return '5'. Next, let's add multiplication and division:
Expression
: Expression 'expression' "+" Number 'number' {expression + number}
| Expression 'expression' "-" Number 'number' {expression - number}
| Expression 'expression' "*" Number 'number' {expression * number}
| Expression 'expression' "/" Number 'number' {expression / number}
| Number 'number' {number}
;
Number
: <number> 'numberToken' {numberToken value asNumber}
;
Here we run into a problem. If you evaluate '2 + 3 * 4' you end up with 20. The problem is that in standard mathematics, multiplication has a higher precedence than addition. Our grammar evaluates strictly left-to-right. The standard solution for this problem is to define additional non-terminals to force the sequence of evaluation. Our grammar with that solution would look like:
Expression
: Term 'term' {term}
| Expression 'expression' "+" Term 'term' {expression + term}
| Expression 'expression' "-" Term 'term' {expression - term}
;
Term
: Number 'number' {number}
| Term 'term' "*" Number 'number' {term * number}
| Term 'term' "/" Number 'number' {term / number}
;
Number
: <number> 'numberToken' {numberToken value asNumber}
;
If you compile this grammar, you will see that '2 + 3 * 4' evaluates to 14 like we would expect. Now, as you can imagine, this gets pretty complicated as the number of precedence rules increases (e.g., C). We can use ambiguous grammars and precedence rules to simplify this situation. Here is the same grammar using precedence to enforce our evaluation order:
%left "+" "-";
%left "*" "/";
Expression
: Expression 'exp1' "+" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 + exp2}
| Expression 'exp1' "-" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 - exp2}
| Expression 'exp1' "*" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 * exp2}
| Expression 'exp1' "/" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 / exp2}
| Number 'number' {number}
;
Number
: <number> 'numberToken' {numberToken value asNumber}
;
Notice that we changed the grammar so that there are Expressions on both sides of the operator. The two lines that we added to the top of the grammar mean that "+" and "-" are evaluated left-to-right and have the same precedence, which is lower than "*" and "/". Likewise, the second line means that "*" and "/" have equal precedence. Grammars in this form are usually much more intuitive, especially in cases with many precedence levels. Just as an example, let's add exponentiation and parentheses. Here is our final grammar:
<number> : [0-9]+ (\. [0-9]*) ? ;
<whitespace> : \s+;
%left "+" "-";
%left "*" "/";
%right "^";
Expression
: Expression 'exp1' "+" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 + exp2}
| Expression 'exp1' "-" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 - exp2}
| Expression 'exp1' "*" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 * exp2}
| Expression 'exp1' "/" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 / exp2}
| Expression 'exp1' "^" Expression 'exp2' {exp1 raisedTo: exp2}
| "(" Expression 'expression' ")" {expression}
| Number 'number' {number}
;
Number
: <number> 'numberToken' {numberToken value asNumber}
;
Once you have compiled the grammar, you will be able to evaluate '3 + 4 * 5 ^ 2 ^ 2' to get 2503. Since the exponent operator is right associative, this expression is evaluated like 3 + (4 * (5 ^ (2 ^ 2))). We can also evaluate expressions with parentheses. For example, evaluating '(3 + 4) * (5 - 2) ^ 3' results in 189.
If you would like to extend the calculator to create abstract syntax trees, you can visit the ASTs page. If you want more information on other SmaCC options, you can visit the directives, scanner, and parser pages.